数组知识点回顾
声明Java数组时,会在内存中开辟一块连续指定大小的空间,用来存储固定大小的同类型元素
在java中定义个名为scores,长度为8,类型为int类型的数组如下:
1
2
3
| public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] scores = new int[8];
}
|
为了便于理解,我们看下它在内存的中的分布示意图:
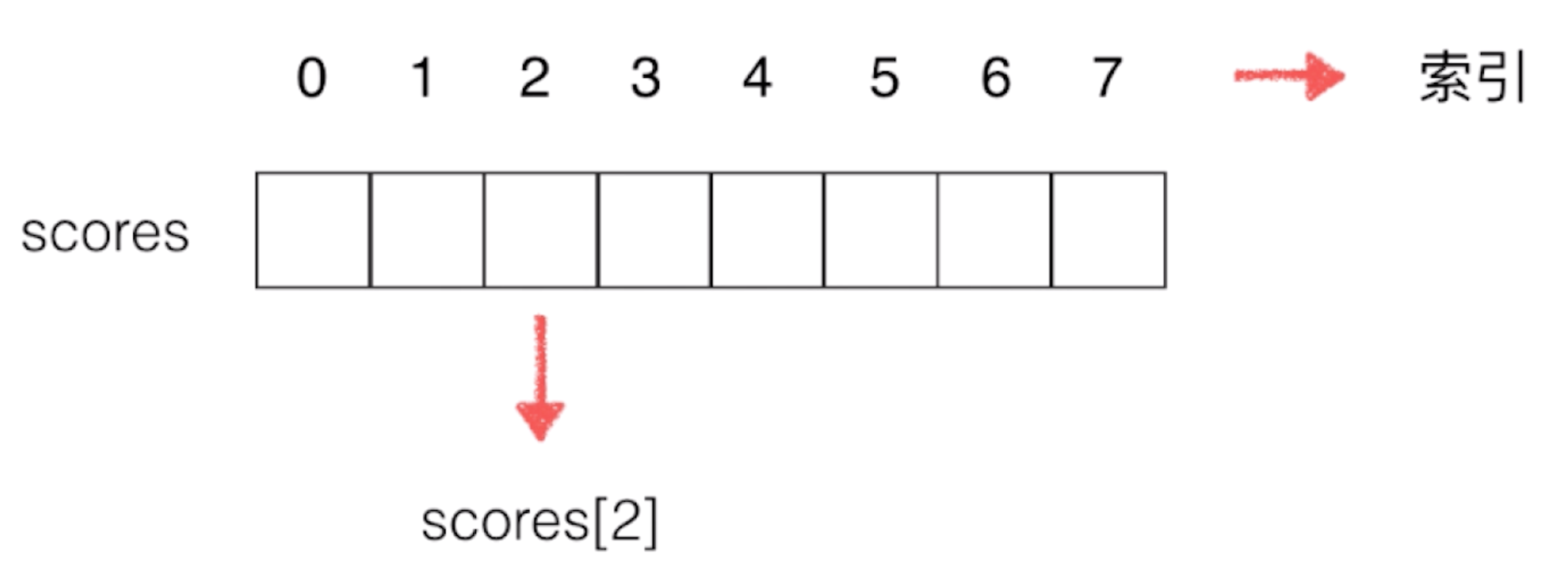
图中的一个个小格子是用来存放数组的元素,小格子上方的0-7数字,是数组中每个元素的下标(也可以叫索引),如果我们要查询数组中指定位置的元素,我们可以通过数组名[索引]来获取,比如图中的scores[2]
在图中我们还可以看到,数组的起始下标是从0开始的(也就是第一个元素),最后一个元素的下标是7(也就是数组的长度8减1)由此类推,数组长度若是n,那么数组最后一个元素的下标是n-1(数组的起始下标总是从0开始的)
各位不要闲唠叨哈,为了照顾所有人(其实我的内心是很纠结的。。。😆)
自定义数组类
思路分析
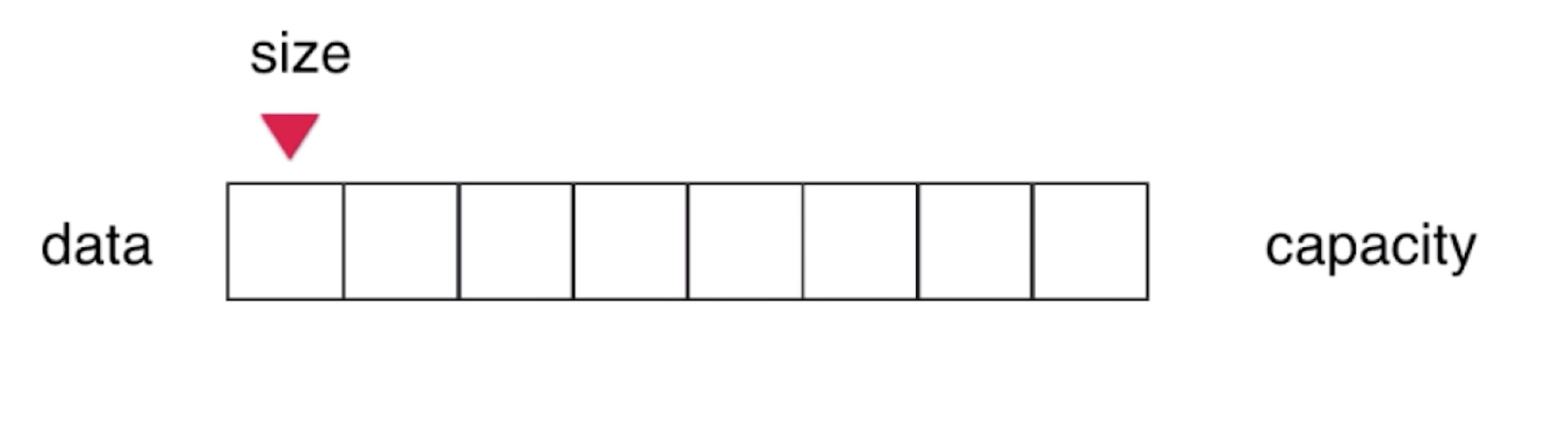
使用data属性表示存放数组的元素,
使用capacity属性表示数组的容量(等价于数组的长度),但是真正自定义数组类的时候我们不需要显示声明,因为隐示等价于(Array.length)
使用size属性表示数组中真正存放元素的个数(注意和capacity概念的区分)。
我们画出示意图:
下面我们来完成初始代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
| public class ArrayExample {
private int data[];
private int size;
public ArrayExample(int capacity) {
data = new int[capacity];
size = 0;
}
public ArrayExample() {
this(10);
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public int getCapacity() {
return data.length;
}
}
|
向数组中添加元素
向指定位置添加元素
假设现在数组的形态是这样,我们需要将77元素插入到索引为1的位置
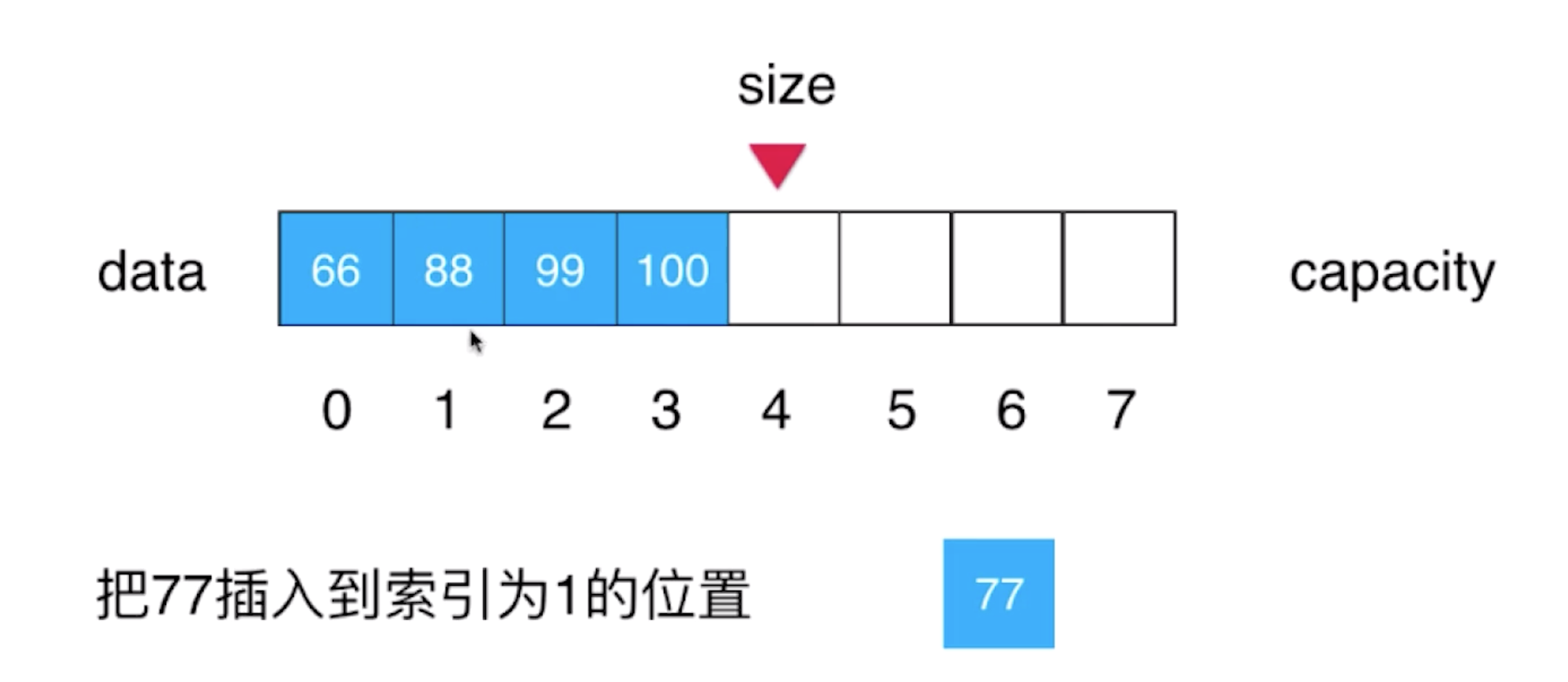
思路分析:把当前索引为1的位置元素以及后面的元素都向后挪一个位置,然后将77这个元素放到索引为1的位置(注意:挪位置的时候,我们应该从最后一个元素100向后挪一个位置,换句话说从后往前挪),完成之后,维护一下size的索引,进行size++操作(size是始终指向数组中下一个没有元素的位置)
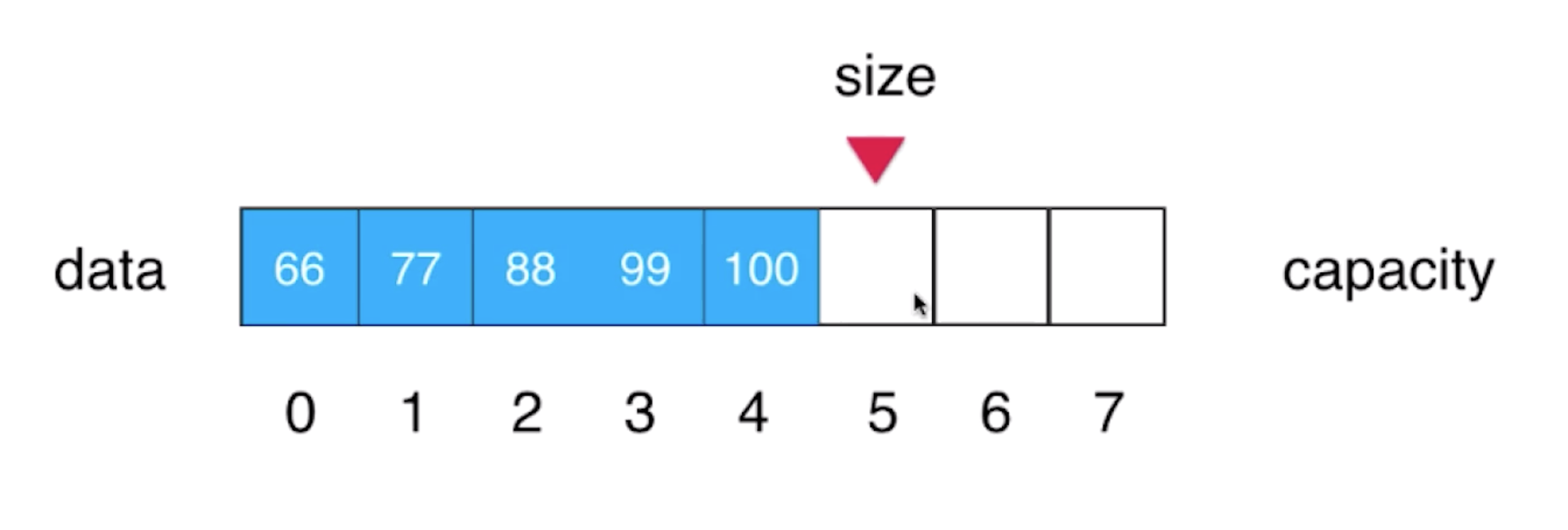
下面我们基于前面写的代码,来完成数组元素的添加操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
public void add(int index, int element) {
if (size == data.length) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("数组添加失败,数组已满");
}
if (index < 0 || index > size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("index索引不合法");
}
for (int i = size - 1; i >= index; i--) {
data[i + 1] = data[i];
}
data[index] = element;
size++;
}
|
由于方面大家查看,只贴出添加数组元素的代码,本文文末,会贴出完成的代码示例地址
现在如果我们想把一个元素添加到数组头部的位置或者尾部的位置,我们可以这么做
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
|
public void addFirst(int element) {
add(0, element);
}
public void addLast(int element) {
add(size, element);
}
|
大家一定要注重代码的复用性哈
查询数组元素和修改数组元素
查询数组元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public int get(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("获取失败,索引不合法");
}
return data[index];
}
|
修改数组元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
|
public void set(int index, int element) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("获取失败,索引不合法");
}
data[index] = element;
}
|
包含数组元素和搜索数组元素
包含数组元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
public boolean contains(int element) {
return Arrays.stream(data).filter(x -> x == element).findAny().isPresent();
}
|
这里使用了Java8的lambda表达式,不知晓的盆友,可以自行去了解一下
搜索数组元素
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
public int find(int element) {
for (int i = 0; i < data.length; i++) {
if (data[i] == element) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
|
删除数组中的元素
现在我们要删除索引为1的元素77
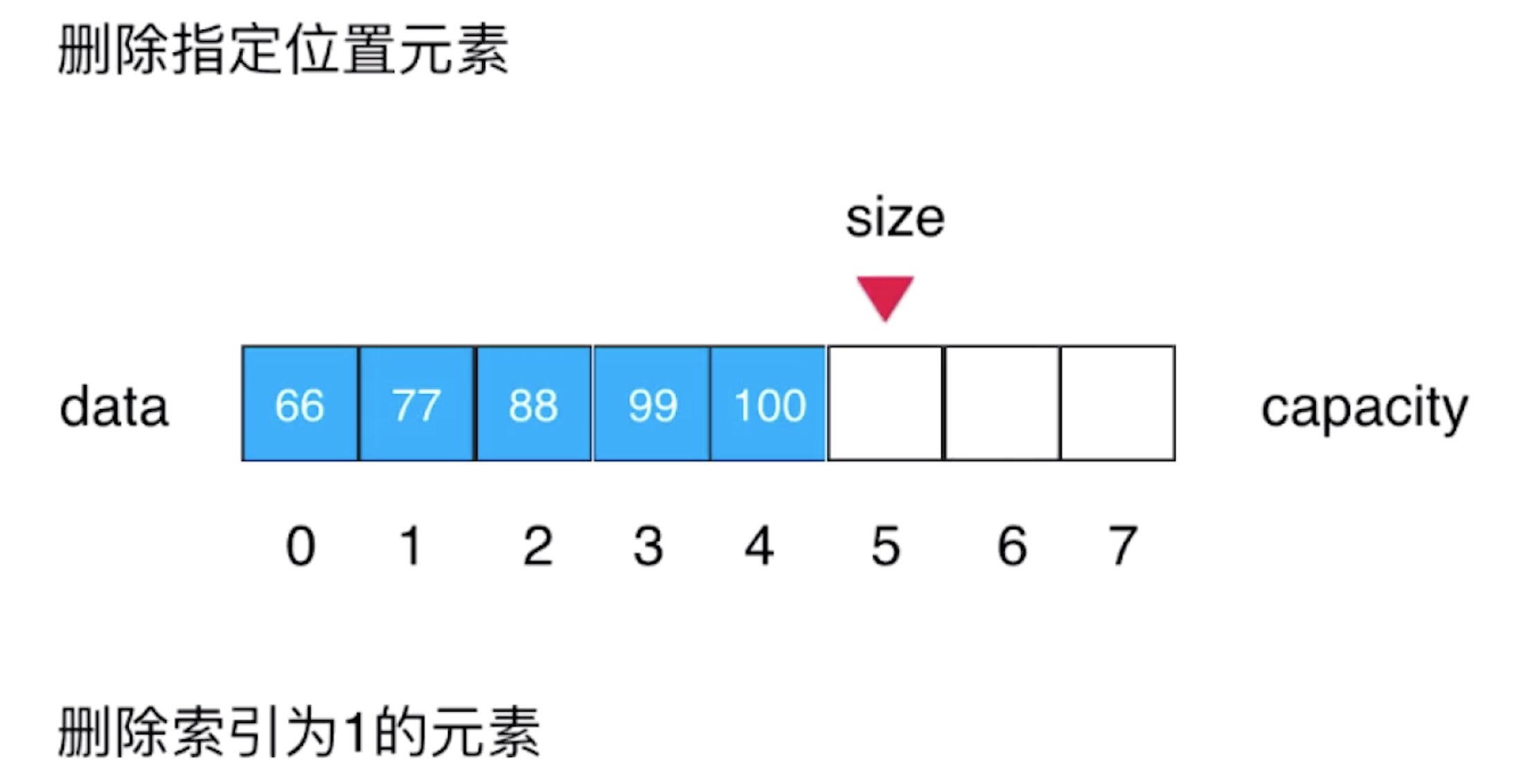
思路分析:我们知晓了数组的插入思路,那么数组的删除思路,刚好和数组的插入思路相反,如果要删除索引为1位置的元素77,我们只需要,从索引2开始,将索引2位置的元素向左移动到索引为1的位置,也就是将索引2位置的元素的值赋值给索引为1位置的元素(等价于data[1]=data[2]),依次类推,将索引为3位置的元素,移动到索引为2位置的元素,一直到最后一个元素,比如图中的元素100,完成之后,这时候,我们需要再次维护一下size的大小,我们要进行size--操作
重要 size 既表示数组中元素的大小,又表示始终指向数组中第一个没有元素的位置
代码完成数组的删除操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
|
public int remove(int index) {
if (index < 0 || index >= size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("删除数组元素失败,索引不合法");
}
int result = data[index];
for (int i = index + 1; i < size; i++) {
data[i - 1] = data[i];
}
size--;
return result;
}
|
完成了数组元素的删除操作,我们还可以便捷地为数组添加删除数组中第一个元素的方法和删除数组中最后一个元的方法。
删除数组中第一个元素的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public int removeFirst() {
return remove(0);
}
|
删除数组中最后一个元素的方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
public int removeLast() {
return remove(size - 1);
}
|
至此,我们已经完成了数组的增删改查操作,下面我们写个测试类,来使用一下我们自己写的简单版数组
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
| public class ArrayExampleTest {
@Test
public void testAdd() {
ArrayExample arrayExample = new ArrayExample(5);
System.out.println(arrayExample);
arrayExample.addFirst(1);
System.out.println(arrayExample);
arrayExample.addLast(2);
System.out.println(arrayExample);
arrayExample.add(0, 10);
System.out.println(arrayExample);
}
}
|
运行结果
1
2
3
4
| ArrayExample{data=[0, 0, 0, 0, 0], size=0,capacity=5}
ArrayExample{data=[1, 0, 0, 0, 0], size=1,capacity=5}
ArrayExample{data=[1, 2, 0, 0, 0], size=2,capacity=5}
ArrayExample{data=[10, 1, 2, 0, 0], size=3,capacity=5}
|
完整版代码GitHub仓库地址:Java版数据结构-数组 欢迎大家关注和 Star
本次我们完成的是静态数组的实现,往往静态数组不够灵活,后面笔者会在代码仓库中实现动态数组,就不作为一个篇幅来讲解了,接下来,笔者还会一一的实现其它常见的数组结构。
- 静态数组
- 动态数组
- 栈
- 队列
- 链表
- 循环链表
- 二分搜索树
- 优先队列
- 堆
- 线段树
- 字典树
- AVL
- 红黑树
- 哈希表
- ….
持续更新中,欢迎大家关注公众号:小白程序之路(whiteontheroad),第一时间获取最新信息!!!






